Bringing Healing Across Borders: UVGI’s joining Humanitarian

Date: May 28-June 4, 2025
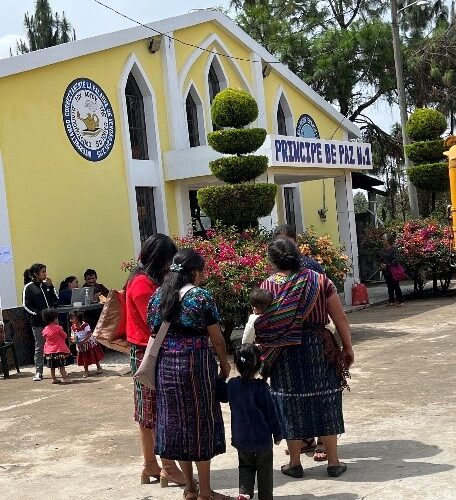
Location: Guatemala City, Guatemala Bola De Oro, Chimaltenango, Guatemala
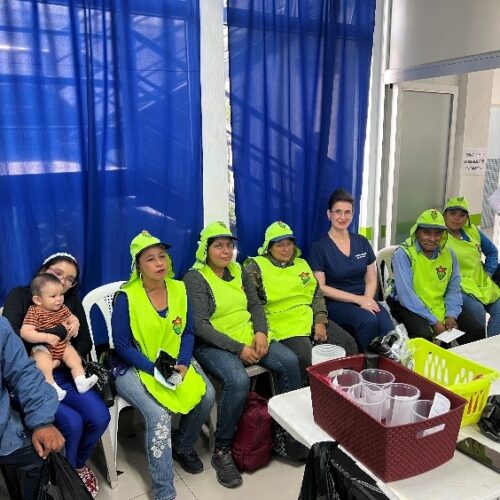
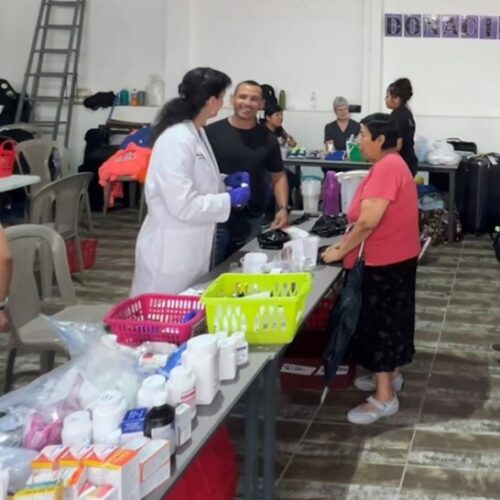
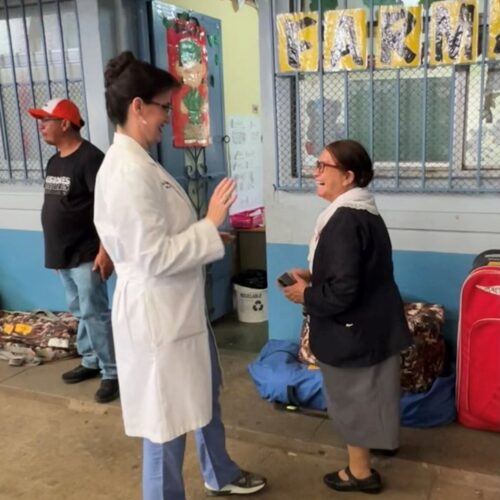
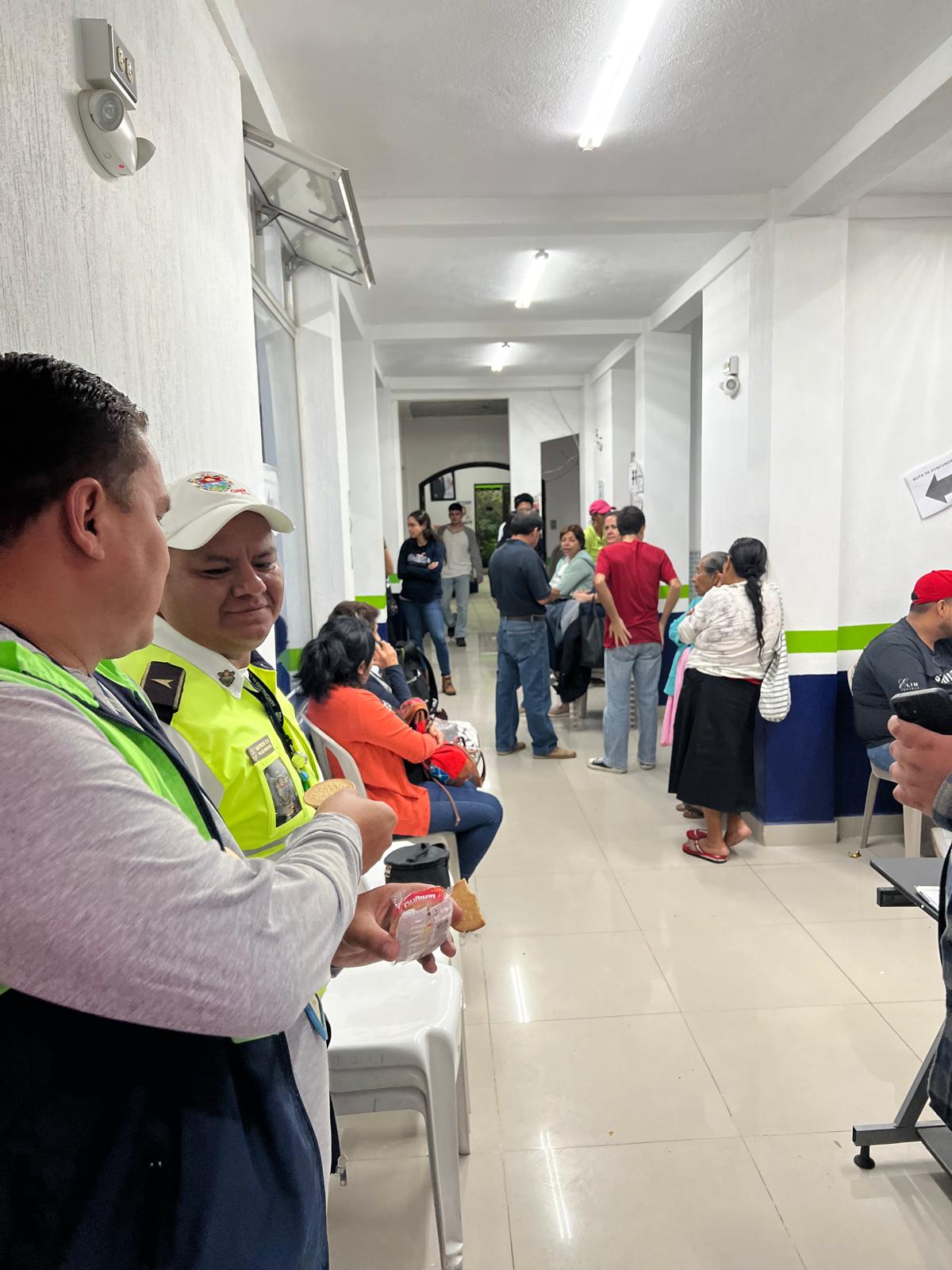
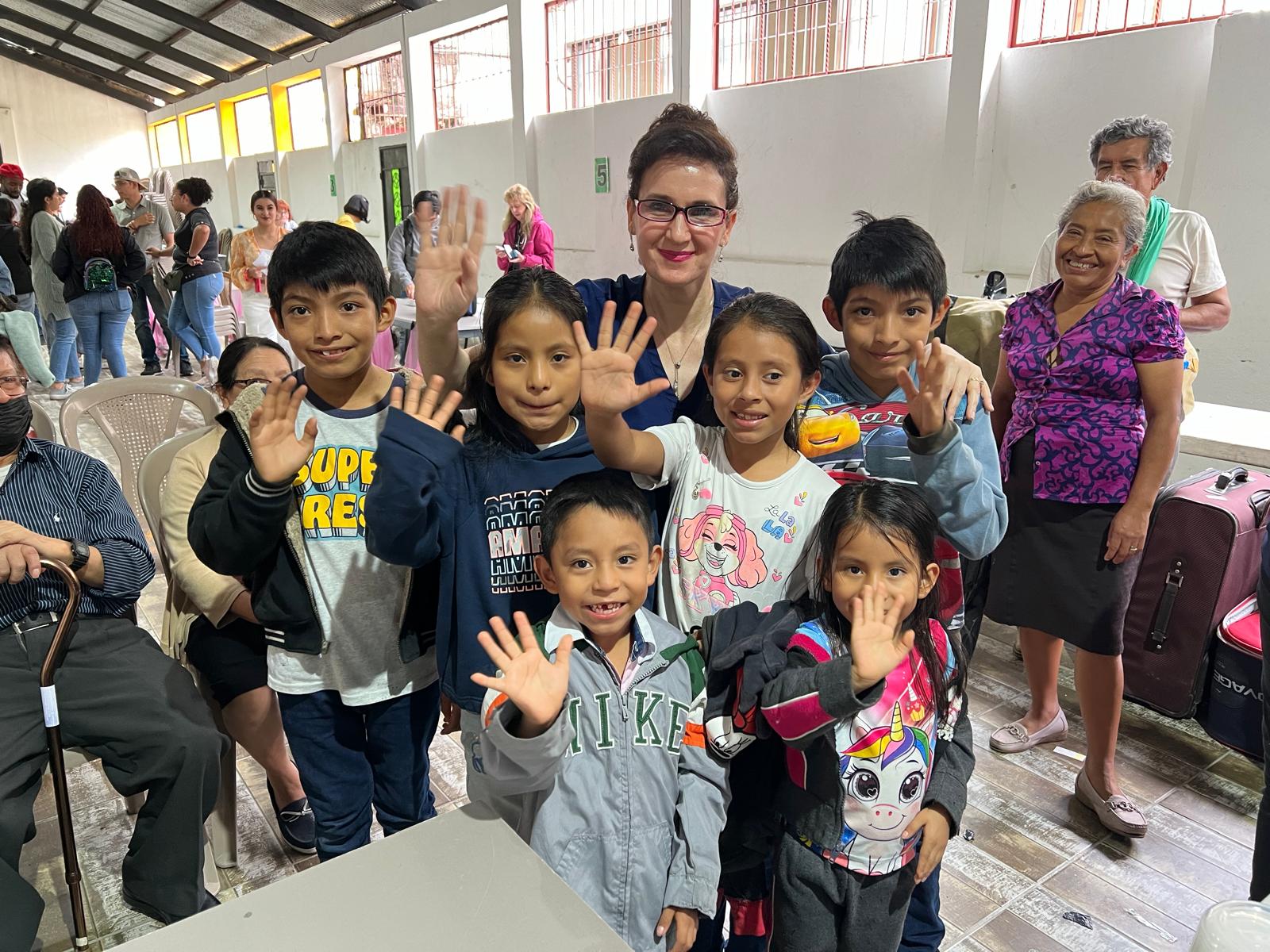
In May 2025, United Voices for Global Impact (UVGI) proudly joined an international humanitarian medical mission to Guatemala City, serving underserved communities and vulnerable populations through a mobile medical clinic—an area where many families have limited essential medical services and face barriers to accessing even basic healthcare.
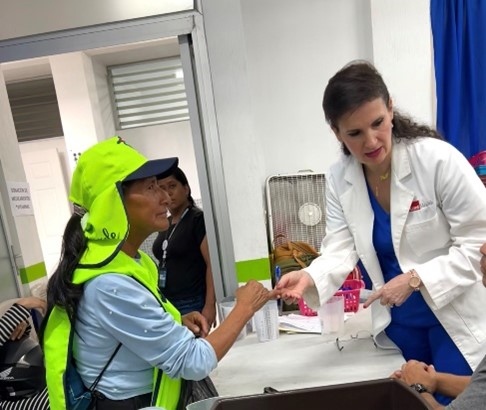
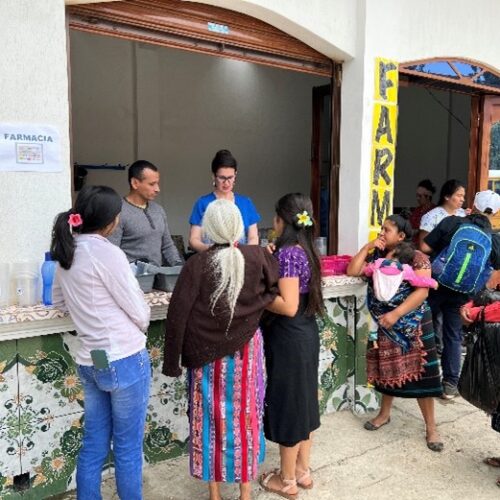
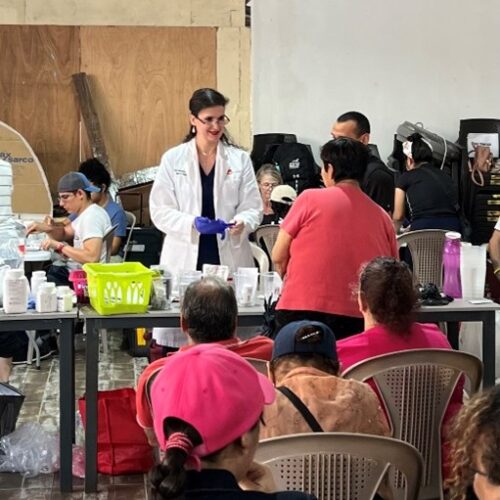
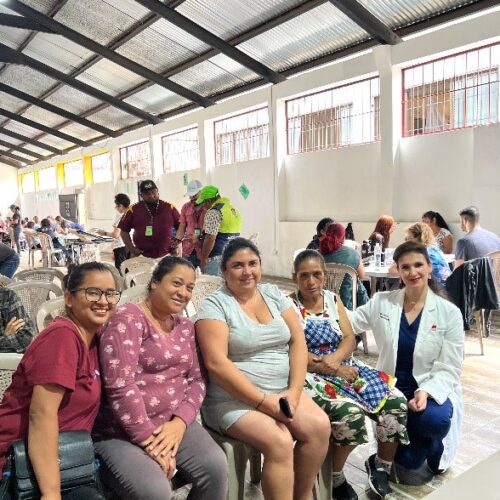
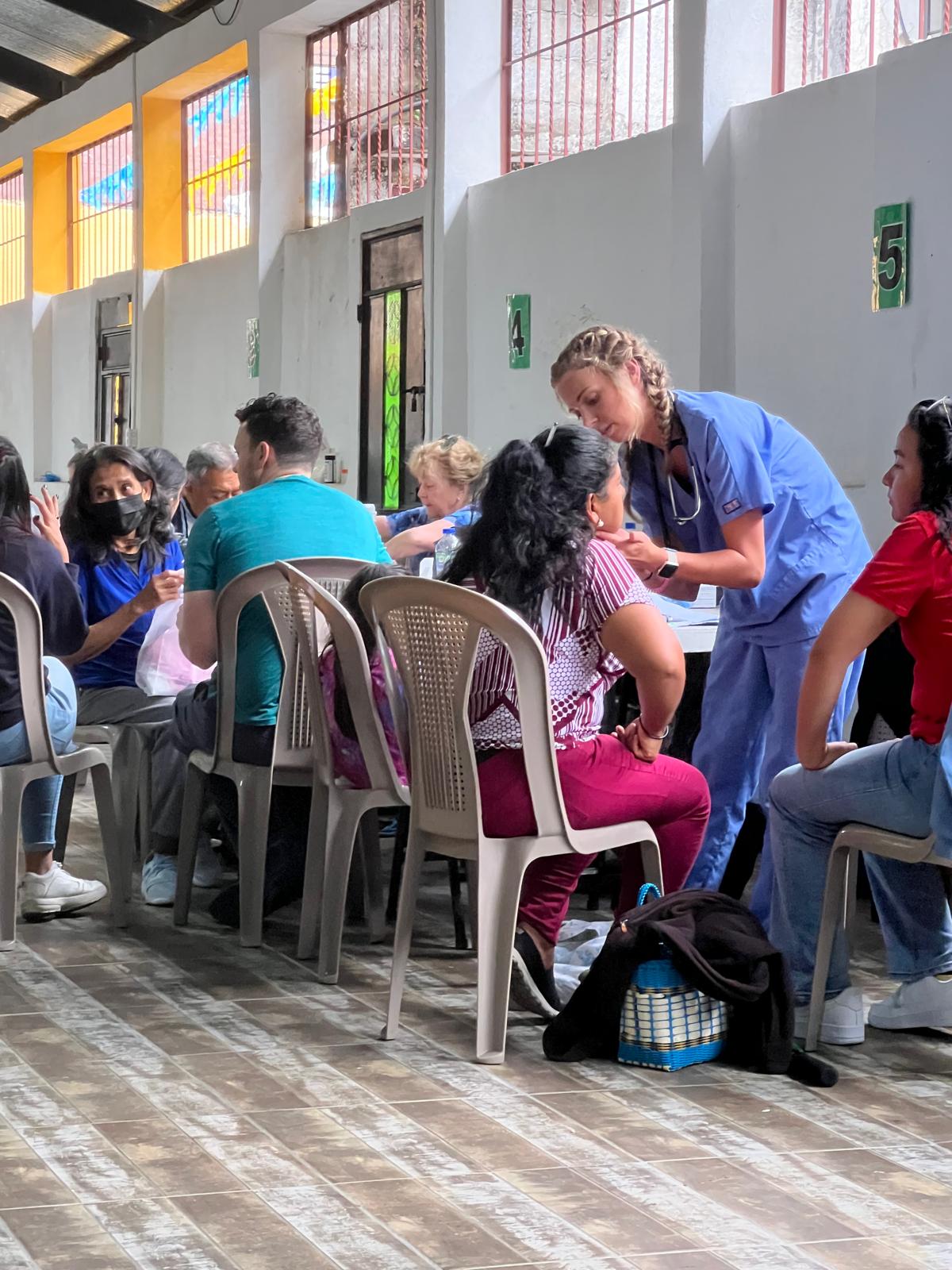
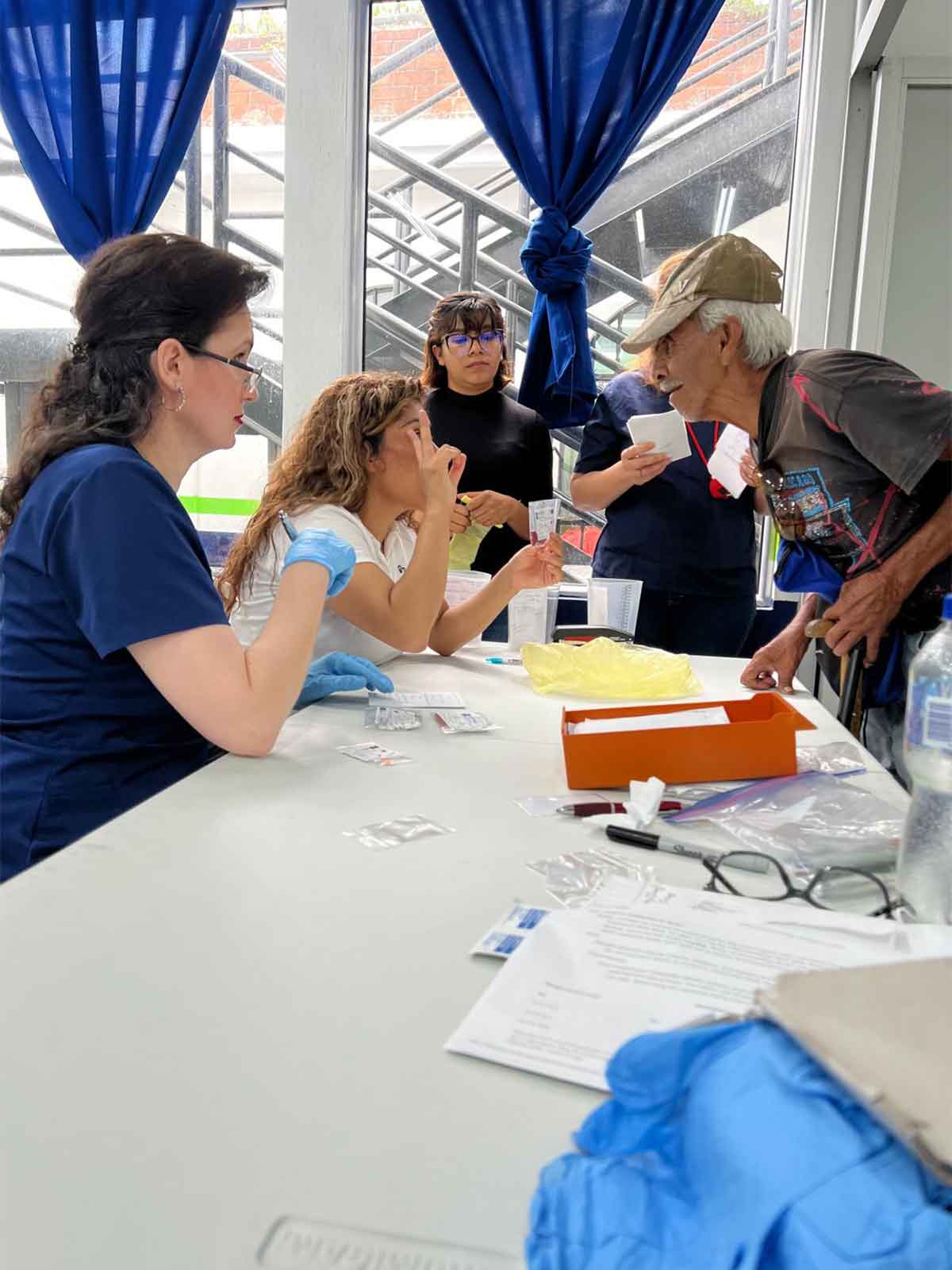
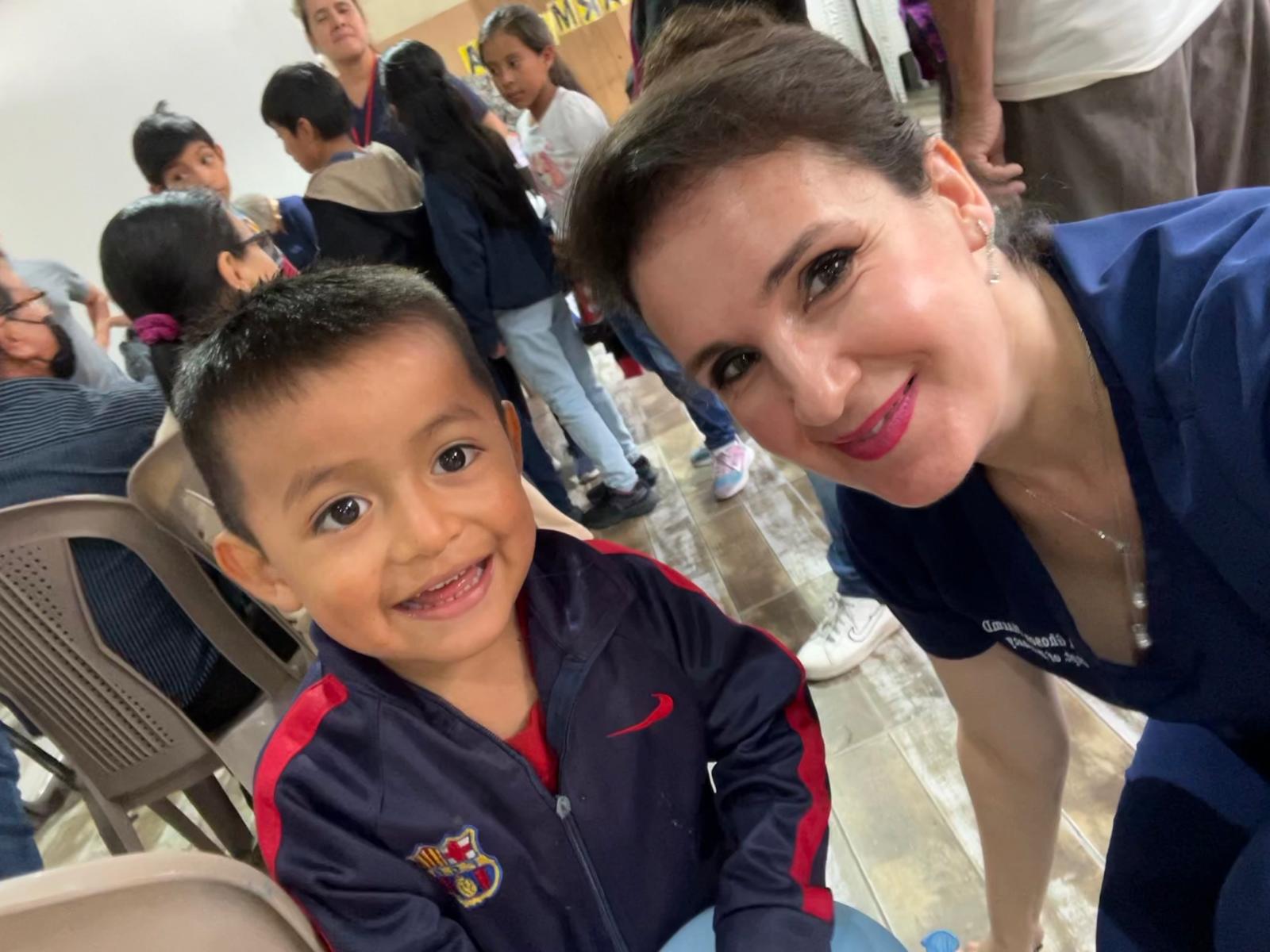
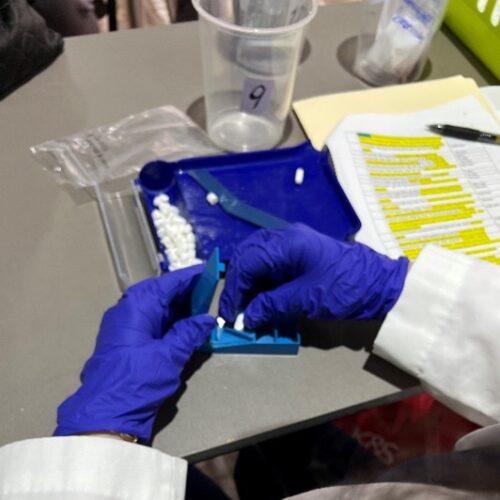
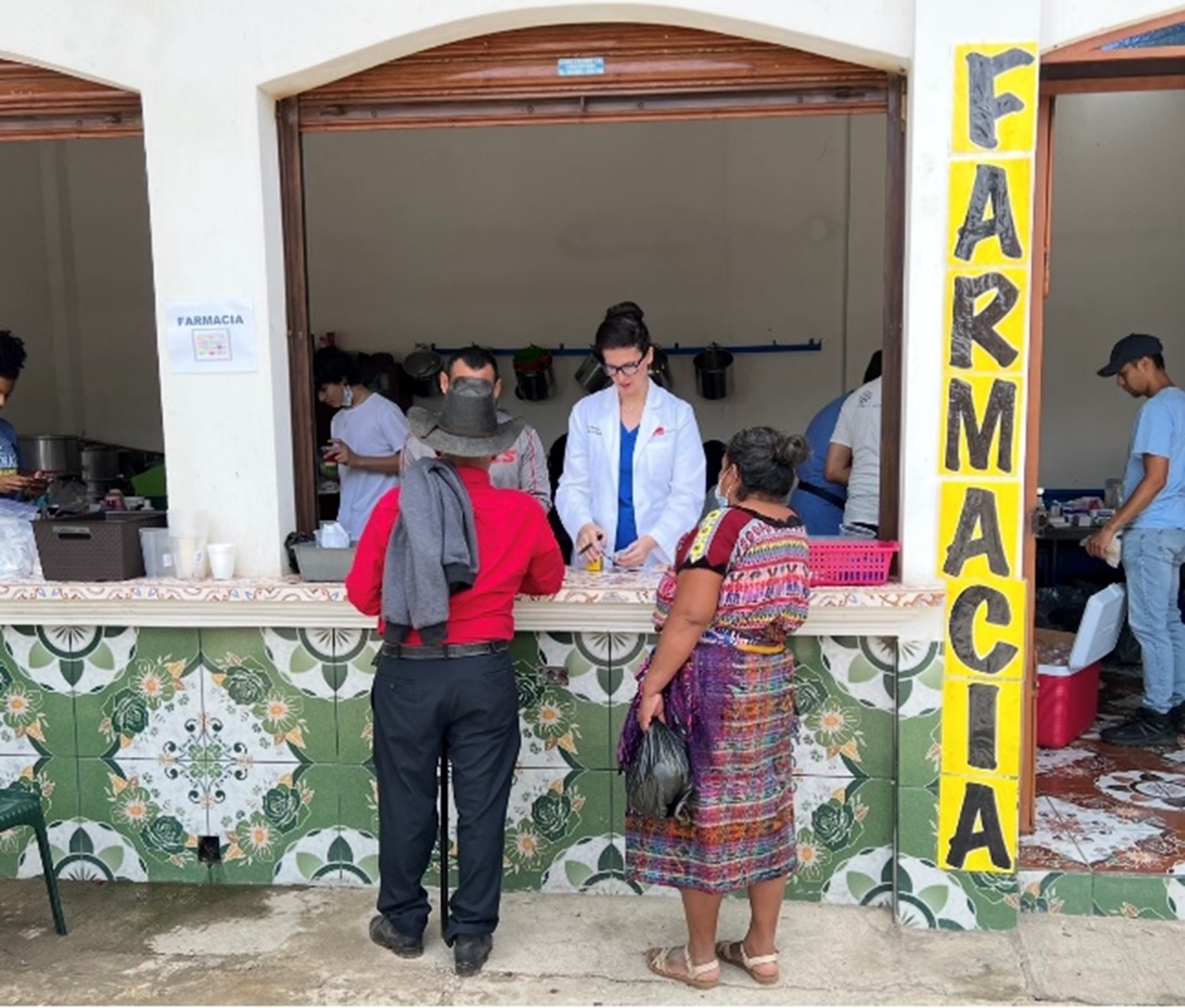
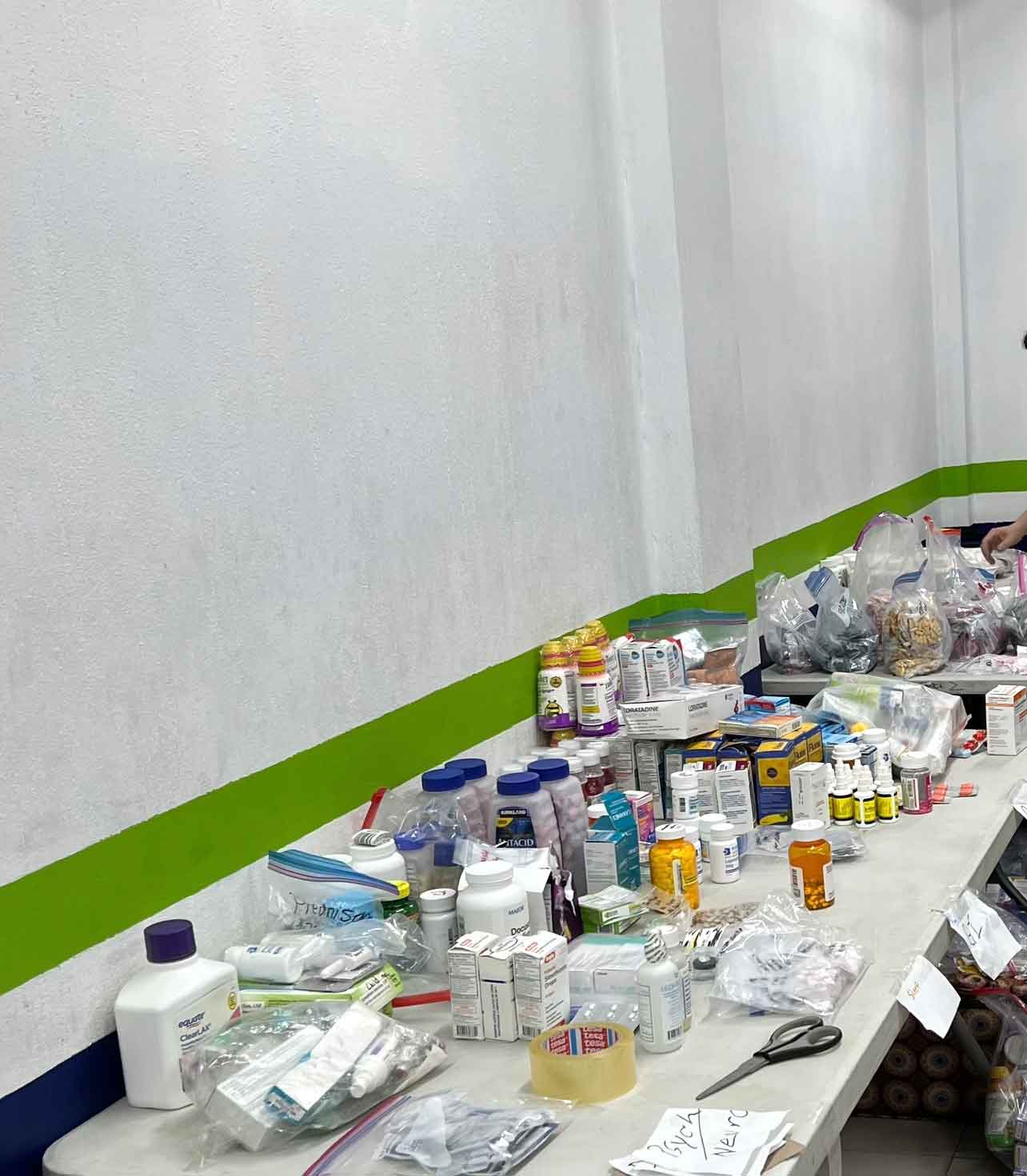
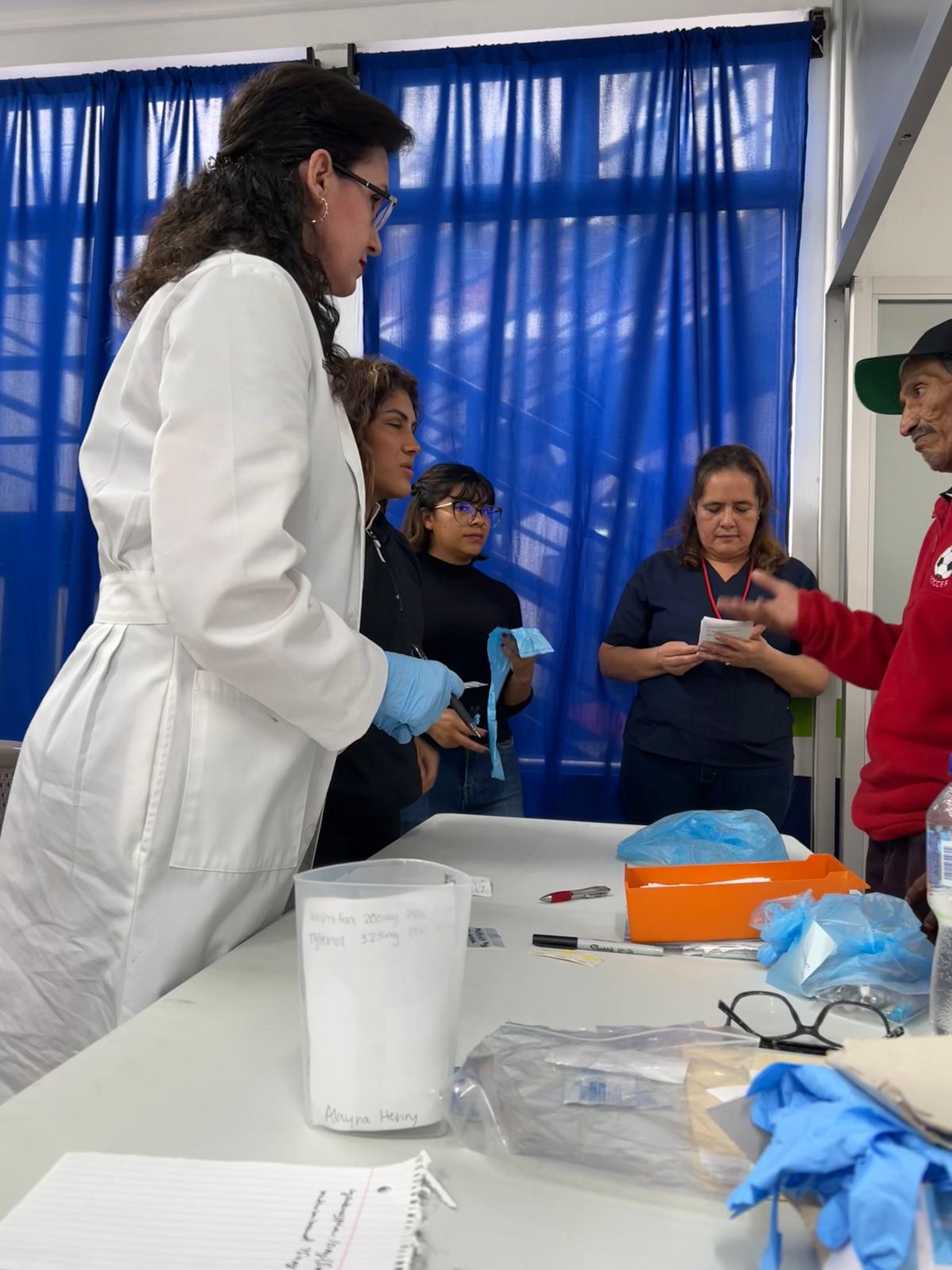
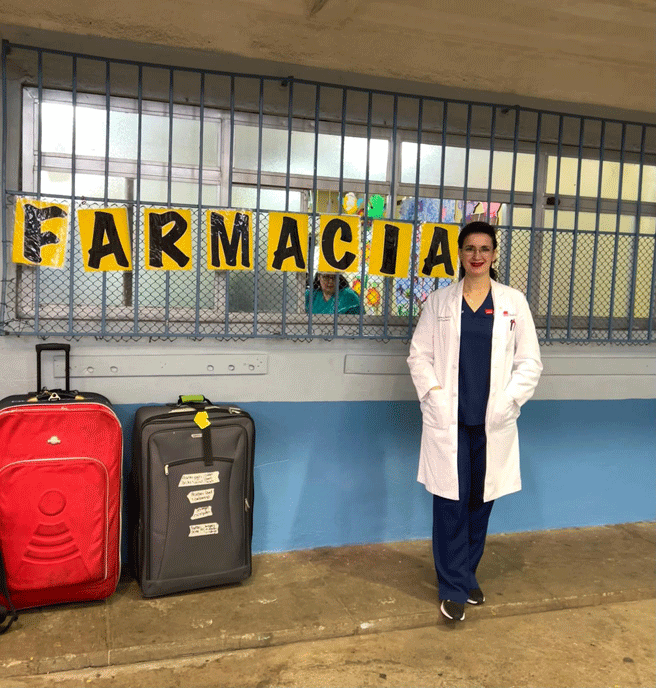
UVGI directly contributed to medication purchases and its President Dr. Hala Ghoson, provided direct pharmaceutical care, health education, counseling and pharmacy services to 1189 patients over the course of several days. Hundreds of prescriptions were filled and explained in detail, ensuring every patient walked away not just with medication, but with knowledge and information on correct use.
Dr. Ghoson personally counseled every patient with the help of interpreters, ensuring safe and effective medication use, and building meaningful, human connections that transcend borders.
“This is why I do what I do—because everyone deserves access to quality healthcare, no matter where they live,” Dr. Ghoson said. “It was a blessing to serve side by side with compassionate healthcare professionals and to witness the strength and warmth of the people of Guatemala.”
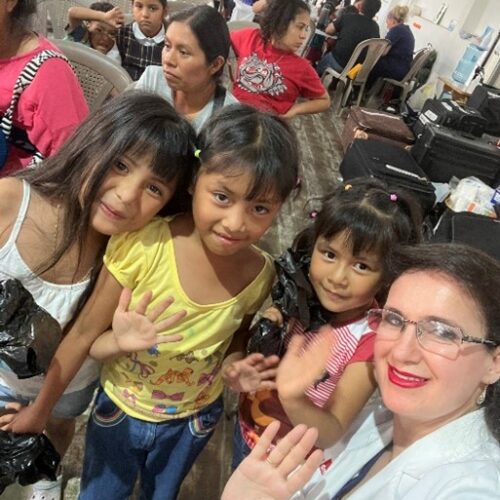
This mobile medical clinic initiative brought much-needed care, compassion, and dignity to over 1,200 patients, with hundreds of prescriptions filled—and lives touched one patient at a time.
Impact Highlights
🏥Over 1,100 patients served
💊Hundreds of prescriptions filled, reviewed and hundreds of essential medications dispensed
🩺Direct health education and counseling provided-100% received one-on-one medication education
🤝Collaboration with a diverse global team of healthcare professionals
💬Culturally sensitive care with interpreter-supported consultations
🎯Focus Area-Chronic care, primary care, pharmacy services, and health education
This mission reflects UVGI’s deep commitment to health equity, especially for underserved communities, and aligns with Sustainable Development Goal 3: Good Health and Well-being. By partnering in humanitarian fieldwork and joining forces of heath care professionals, UVGI continues to extend its reach and respond where the need is greatest—advocating for a world where access to healthcare is a right, not a privilege.
Through this mission and others like it, UVGI stands firm in its mission to:
Empower for Impact. Inspire for Change.
United for Health: Guatemala Medical Outreach

Date: 10-18 June, 2024
Location: Guatemala City, Guatemala
Humanitarian action is central to UVGI mission and understanding the needs of underserved communities and their Lack of healthcare access is essential for effectively addressing these disparities and providing the necessary support and resources.
Our focus on underserved communities drives us to provide essential medical services and medications to those in need. These communities often lack access to critical resources and healthcare, making them more vulnerable to adverse health outcomes. Guided by our core values of COMPASSION and COMMUNITY, and our fundamental belief that all human beings are entitled to basic resources to survive and thrive, we are dedicated to making a positive impact.
Barriers to Underserved Communities
Underserved communities are populations that face significant barriers to accessing essential healthcare services, often due to socioeconomic, geographic, and systemic challenges. These communities can be found in both urban and rural settings and are characterized by a lack of basic resources, limited healthcare infrastructure, and insufficient medical personnel. Multiple factors contribute to the healthcare access issues faced by these communities:
Socioeconomic Barriers
Poverty
Many individuals in underserved communities live below the poverty line, which restricts their ability to afford healthcare services, medications, and health insurance. Without financial resources, even basic medical care can be out of reach.
Education
Limited access to education affects health literacy, making it difficult for people to understand health information, navigate the healthcare system, and make informed decisions about their health.
Geographic Barriers
Remote Locations
Rural and isolated areas often lack healthcare facilities, requiring residents to travel long distances to receive medical attention. This distance can be a significant deterrent, especially in emergencies or for those without reliable transportation.
Urban Underserved Areas
Even within cities, certain neighborhoods may lack sufficient healthcare facilities. These areas might have overburdened clinics and hospitals, leading to long wait times and inadequate care.
Systemic Barriers
Healthcare Infrastructure
Underserved communities frequently suffer from a lack of healthcare infrastructure, including clinics, hospitals, and medical equipment. This shortage hampers the delivery of comprehensive healthcare services.
Shortage of Healthcare Providers
There is often a significant shortage of healthcare professionals willing to work in underserved areas. This shortage results in a high patient-to-provider ratio, reduced access to specialized care, and burnout among existing staff.
Specific Challenges Faced by Underserved Communities
Chronic Diseases
Underserved populations have higher rates of chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases. The lack of regular medical care exacerbates these conditions, leading to complications that could otherwise be managed or prevented.
Preventive Care
Preventive services, such as vaccinations, screenings, and routine check-ups, are less accessible to these communities. This gap increases the risk of undetected illnesses and preventable health issues becoming severe.
Mental Health
Mental health services are often scarce in underserved areas. Without access to counseling, psychiatric care, and support services, individuals struggling with mental health issues may not receive the help they need.
Maternal and Child Health
Pregnant women and children in underserved communities face significant health risks due to inadequate prenatal, childbirth, and pediatric care. This lack of care can lead to higher rates of infant and maternal mortality and childhood illnesses.
Substance Abuse
Substance abuse is a critical issue in many underserved communities, with limited access to rehabilitation and support services exacerbating the problem. Addressing substance abuse requires comprehensive intervention strategies, including education, counseling, and medical treatment.
UVGI’s Role in Addressing Healthcare Access in Underserved Communities
At UVGI, we recognize these challenges and are dedicated to making a difference. Our mission is to provide essential medical services and medications to those who need them the most. Through our partnerships at the global, national and community levels, we focus on:
1. Enhance Healthcare Infrastructure: By joining mobile clinics and partnering with organizations and healthcare providers, we aim to bring medical services directly to underserved areas, reducing the distance and barriers to access.
2. Support Healthcare Providers: UVGI works to support healthcare professionals willing to serve in these communities, providing them with the necessary resources and pharmaceutical education to offer high-quality care.
3. Community Engagement: We engage with community leaders and members to understand their specific needs, ensuring our efforts are culturally sensitive and effectively address the unique challenges faced by each community.
4. Promote Health Education: By focusing on pharmaceutical care and medication/vaccine education, we empower individuals to make informed health decisions, understand the importance of preventive care, and effectively manage chronic conditions. Our education on pharmacy and medication management includes:
Medication Understanding: We educate patients on the proper use of their medications, including understanding dosage instructions, recognizing potential side effects, and knowing what to do in case of missed doses.
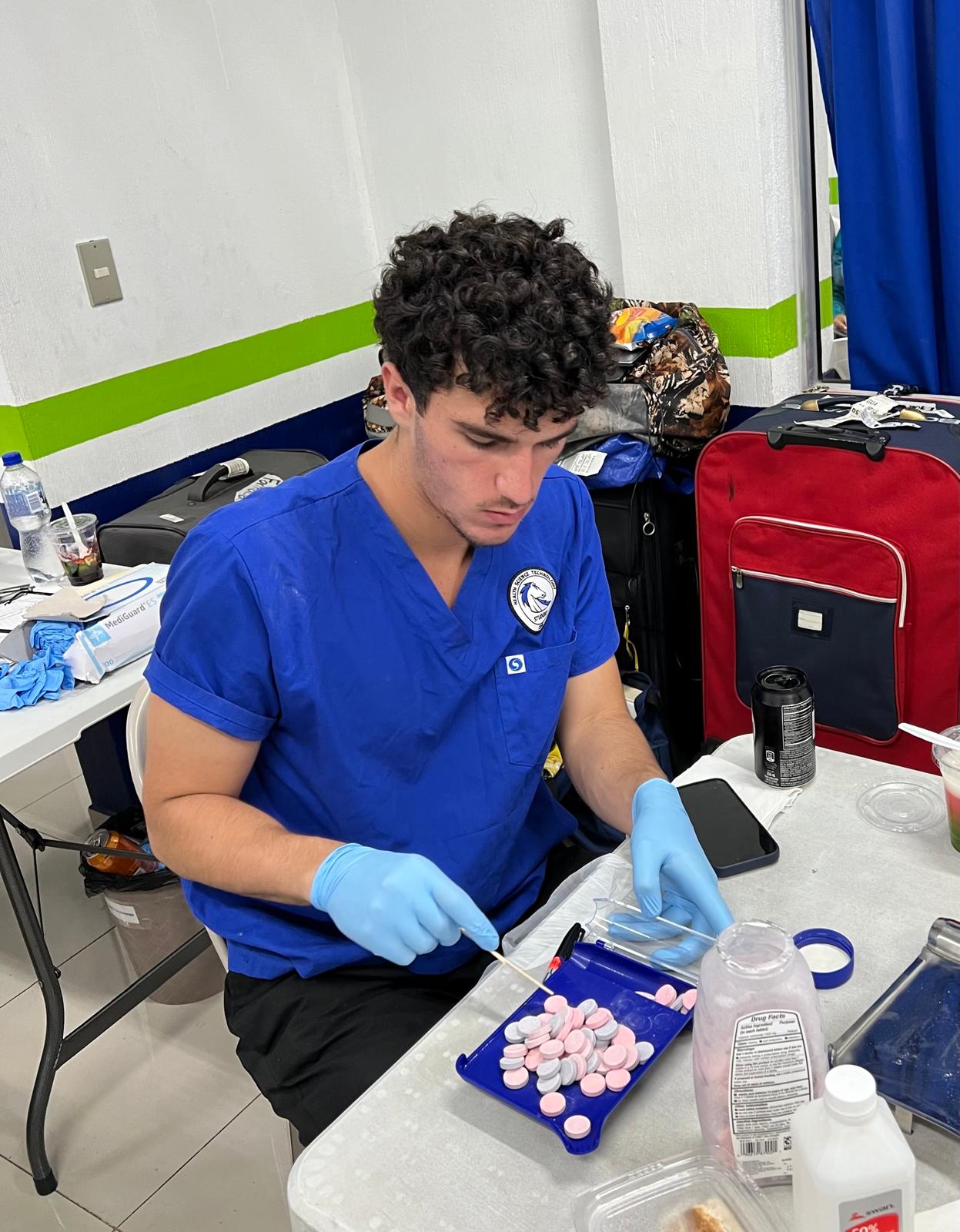

Safe Usage and Storage: UVGI teaches safe medication practices, such as the importance of following prescribed regimens, avoiding sharing medications, and proper storage to maintain drug efficacy and prevent accidental ingestion, especially by children and inform about drug interactions, side effects, and allergies.
Adherence to Prescriptions: We emphasize the importance of adhering to prescribed medication regimens, particularly infections and chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases, to manage symptoms effectively and prevent complications.


Preventive Medication: Education on the role of preventive medications, such as vaccines and prophylactic treatments, helps individuals understand their importance in preventing illnesses and maintaining overall health.
Through these targeted educational efforts, we ensure that individuals in underserved communities not only receive necessary medications but also possess the knowledge to use them safely and effectively, leading to better health outcomes and improved quality of life.
OUR IMPACT
Our participation in humanitarian medical mission in Guatemala and joining forces to bring medical aid to underserved communities provided much-needed medical care in these areas.
We have had the privilege of working alongside healthcare professionals, assisting communities with limited access to healthcare, providing medications and pharmaceutical care to hundreds of patients in Guatemala City. Our efforts included participation in clothes drive, medications purchase, dispensing and offering professional pharmaceutical services to ensure patients received the necessary medications, proper dosages, and comprehensive information on safe usage. Serving hundreds of patients, spanning a diverse range from pediatric to adult and elderly individuals and attending to numerous medical needs was our priority. We will continue to providing essential medical services to those who need them the most, contributing to better health outcomes for underserved communities and the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-development-goals/